Overcoming climate change
Overcoming climate change
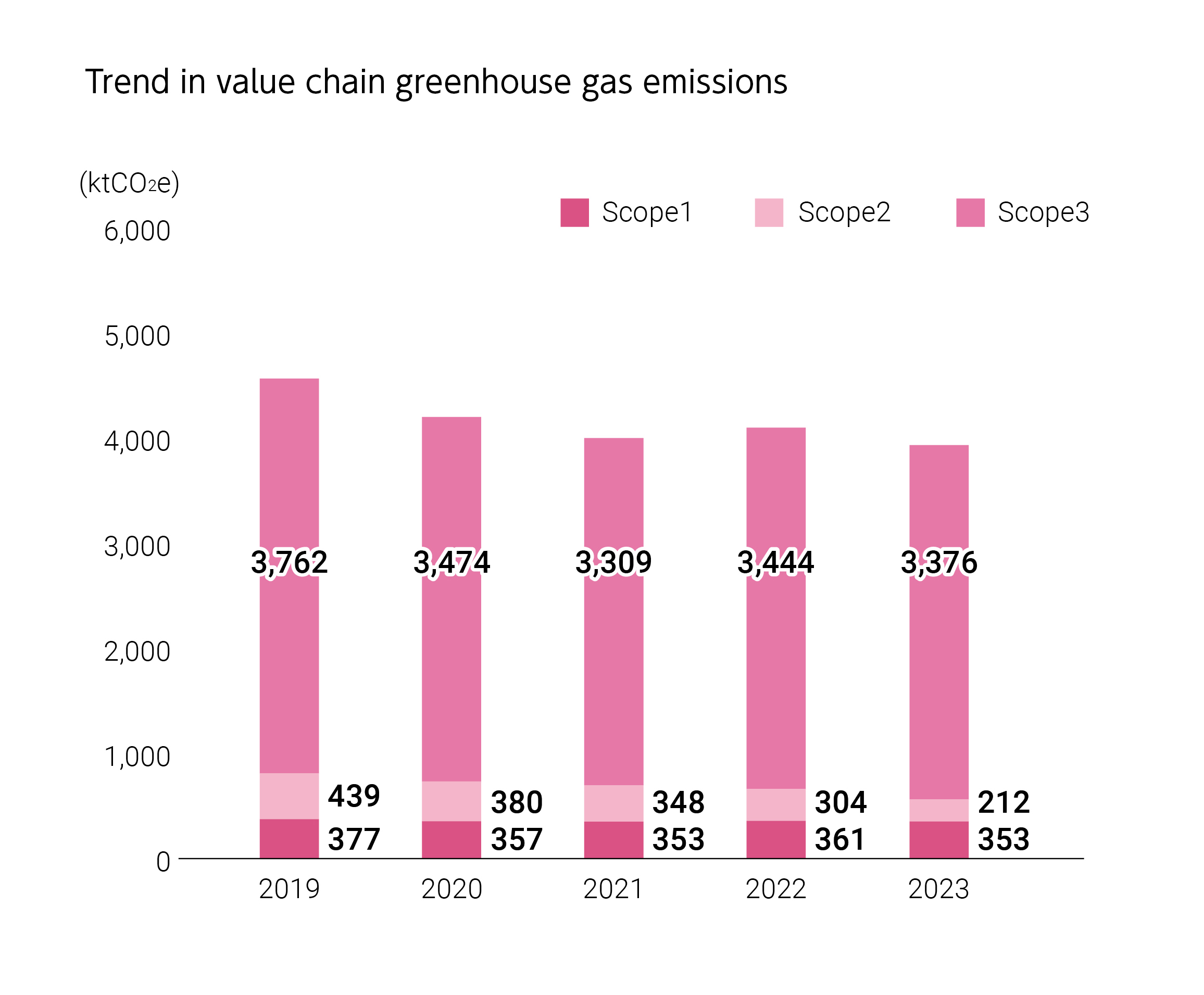
The Kirin Group was one of two companies that represented Japan when we presented our environmental measures to the world at the third session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Kyoto in 1997. The Kirin Group has long been working to reduce GHG emissions. The group set an ambitious target of “reducing GHG emissions across the entire value chain by half from the 1990 level by 2050” in 2009. The group recognizes impacts of climate change on natural capital, such as agricultural raw materials and water, by applying scenario analysis based on the TCFD recommendations. The group sets science-based targets for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, and declares its aim to switch to 100% renewable energy for electric power used by 2040, and commits Net-Zero GHG emissions by 2050. In order to lead the way in creating a decarbonized society, we have been focusing on the processes involved in these efforts. We will steadily implement integrated initiatives to reduce GHG emissions, with respect for natural capital and while promoting containers and packaging initiatives.
Main Activities
- Our long-term target to achieve Net-Zero GHG emissions across the entire value chain by 2050 certified as a science-based Net-Zero target (July 2022: the first case in food and beverage industry in the world) Obtained approval for the science-based 1.5℃ target (2020)
- Joined RE100 (2020) and set a target for renewable electricity use: 100% by 2040. Participated in Policy Working Group of RE100, and sent, as the working group, a policy proposals, e.g. expansion of renewable electricity infrastructure, to Japanese Government, aiming to achieve the 1.5℃ target.
- Achieved 100% renewable energy in purchased electricity at Kirin Brewery’s all production and sales sites (two plants in 2022, three plants in 2023, and four plants and all sales sites in 2024), Kyowa Kirin Takasaki Plant, Ube Plant, research laboratories, etc., and Lion's plants in Australia and New Zealand (2023).
- Introduced large-scale photovoltaic system to nine Kirin Brewery plants (~2023, including eight breweries and plants with PPA model purchasing), Mercian Fujisawa Plant (2023), Kyowa Kirin Ube Plant (2023), Kyowa Hakko Bio Hofu Plant (2024), and Lion Castlemaine Perkins (2019)
- Launched the Kirin Supply Chain Environmental Program (2024)
Targets and Progress
Reduction in GHG emissions
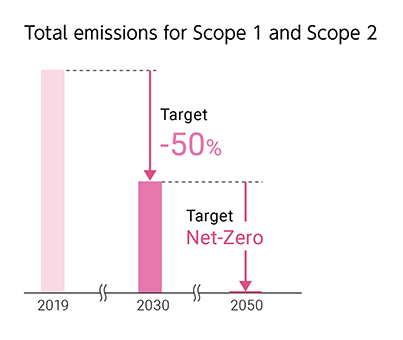
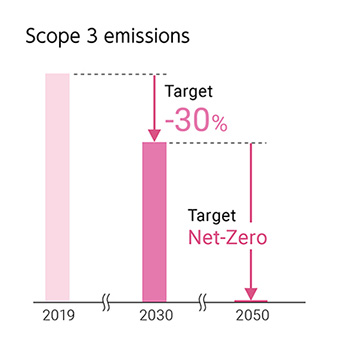
2050 Net-Zero (Environment Vision 2050)
2030 Scope 1 + 2 down 50% and Scope 3 down 30%
(compared with 2019) (SBT for 1.5℃ target*)
2024 Scope 1 + 2 down 23% (compared with 2019) (non-financial target)
- In December 2020, we upgraded our previous “SBT for 2℃” target,and received approval for our “SBT for 1.5℃” target.
Actual results
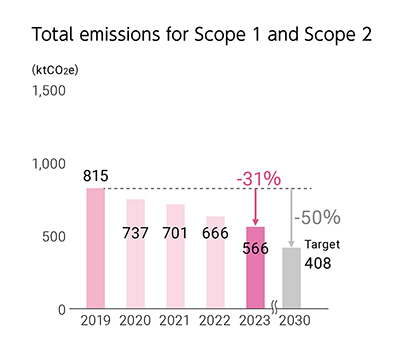
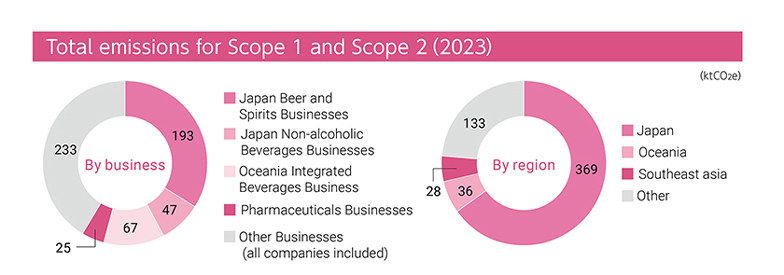
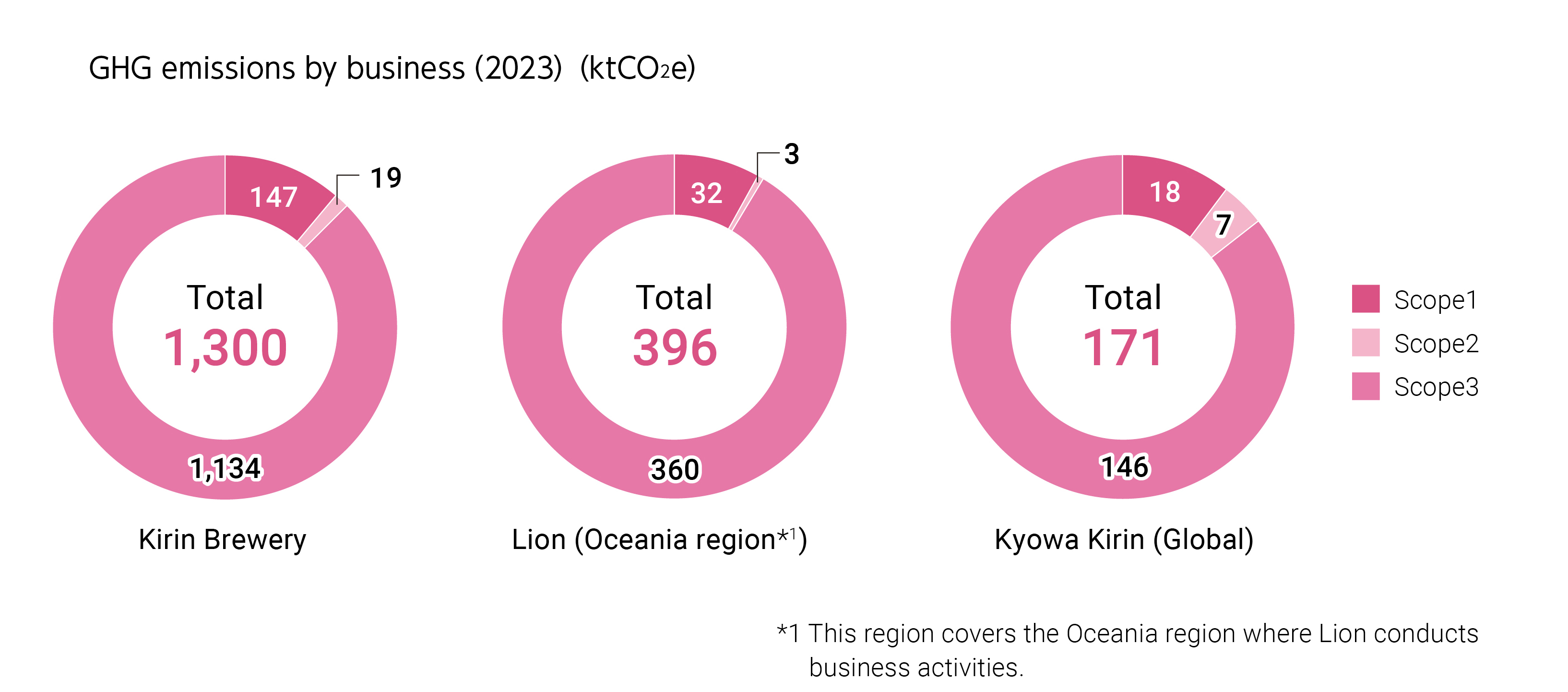
Total emissions for Scope 1 and Scope 2(2023)
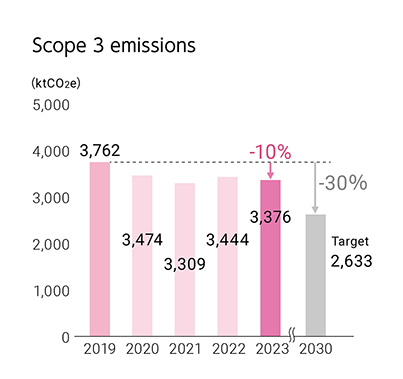
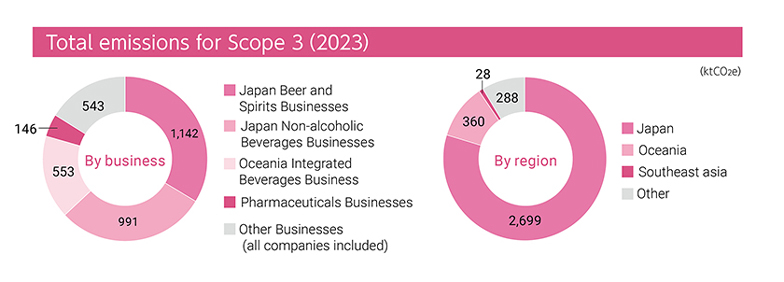
Total emissions for Scope 3(2023)
- Kirin Holdings’ new mid-term GHG reduction target was approved by the Science Based Targets initiative based on 1.5℃ criteria
- Kirin Group joined RE100 Renewable Electricity Initiative Companywide use of 100% renewable electricity by 2040
- Kirin Holdings’ long-term GHG reduction target was approved by the Science Based Targets*1 initiative based on science-based net-zero targets
- Kirin Holdings Selected As “CDP Supplier Engagement Leader” Also Receives The Highest “A-List” Rating In The “CDP Climate Change and Water Security” For 2022
Raw materials
Measures in tea farms for adapting to climate change
The Kirin Group contributes to Sri Lankan tea farms’ measures for adapting to climate change through training programs for Rainforest Alliance Certification. Specifically ,Rainforest Alliance and Kirin Holdings promote tea farms to plant cover crops, grasses crawl on the ground, with deep roots on steep slopes. The cover crops prevent runoff of soil from erosion by torrential rain and falls in tea leaf production volumes.
Importing wine in large bags
Mercian imports some of its wine via marine transportation in specially designed 24kl bags (equivalent to about 32,000 of 750ml bottles) with low oxygen permeability and fills the wine into bottles in Japan. Compared to importing bottled wine, this method reduces Mercian’s GHG emissions from marine transportation by roughly 60% by eliminating needs to transport heavy bottles by sea. Bottling in Japan enables us to use Ecology Bottles (made with at least 90% recycled glass), lightweight bottles, and PET bottles as containers. This production system reduces resource consumption and GHG emissions significantly throughout the value chain.
-

Specially designed large bags
In-line blow aseptic filling machine
In the past, we purchased empty PET bottles from container manufacturers and shipped them to plants where we filled them with beverages. With in-line blow aseptic filling machines, we mold PET bottles from preforms, thick, compact, semi-processed bottle, in our production processes and fill them under aseptic conditions. This system reduces GHG emissions of empty bottle transportation since trucks can carry much more preforms than empty molded PET bottles. In 2003, we installed preform molding equipment to a beverage production line at Kirin Distillery, the first case in Japanese beverage industry, reducing transportation loads of preforms.
At the Kirin Beverage Shonan Plant, in 2021, we switched our high-pressure compressors for PET bottle molding from V-type reciprocating compressors to screw compressors and horizontally opposed reciprocating compressors with variable frequency drives, thereby reducing annual power usage by around 8%. These machines enable us to recover waste heat from themselves and to reuse the heat to other processes.
- The information and product images above are as of the end of June 2023.
Renewable energy
Switch purchased electricity for plants to 100% renewable
Kirin Brewery has achieved 100% of renewable energy for purchased electricity at Sendai and Nagoya Breweries since 2022, Fukuoka and Okayama Breweries since January 2023, Toride Brewery since April 2023, and Hokkaido Chitose, Yokohama, Shiga, and Kobe Breweries, as well as all sales sites, since January 2024. As a result, Kirin Brewery has achieved 100% renewable energy for purchased electricity at all production and sales sites, and the proportion of renewable energy in all electricity usage is 66%. We aim to achieve RE100 target as soon as possible and replace all electricity used in our global operation to renewable energy in the future.
Kyowa Kirin completed to switch purchased electricity to renewable of its manufacturing sites and research laboratories in Japan. Kyowa Kirin expanded the initiative from Takasaki Plant, Bio Production Technology Laboratories, Fuji Research Park, and CMC Research Center, in 2020, to Ube Plant in 2023. Through these initiatives, Kyowa Kirin reduced CO2 emissions from its operation by 55% by the end of 2023 compared with those of 2019.
Since January 2022, all “Château Mercian” wineries (Château Mercian Katsunuma Winery, Château Mercian Mariko Winery, and Château Mercian Kikyogahara Winery) have achieved 100% renewable energy by applying renewable energy certificates with purchased electricity. At breweries in Australia and New Zealand for Lion, 100% of purchased electricity has been sourced from renewable energy since February 2023.
- Kyowa Kirin Has Introduced RE100 Renewable Electricity to All Purchased Electricity at Its Two Plants and Three Laboratories
- Kirin Brewery Completes Installation of Large-scale Solar Power Generators At All Domestic Breweries
- Sunshine State’s XXXX Brewery Now 100 Per Cent Solar Powered
Use of large-scale solar power generation
Kirin group values, in its renewable energy procurement, “additionality,” which refers to creating new sources of renewable energy in the world, as well as “ethical procurement,” which refers to considering the environmental impact and human rights in generating energy.
Kirin Brewery has introduced large-scale photovoltaic system at all nine plants (eight plants, excluding Yokohama Plant, use PPA model*) At Mercian Fujisawa Plant, we introduced photovoltaic electricity based on PPA model from March 2023. This initiative will reduce annual GHG emissions by approximately 124 tonnes, and increase the proportion of renewable energy in electric power used by Mercian as a whole from approximately 5% at present to approximately 8%.
At Kyowa Kirin, we have introduced large-scale photovoltaic system (1.47 MW) based on PPA model at Ube Plant in 2023. This initiative reduced annual CO2 emissions by approximately 1,029 tonnes.
Kirin Group Logistics, Kyowa Hakko Bio, and Shinshu Beverage have leased parts of their land and building roofs to photovoltaic generation businesses, contributing to both effective use of their assets and expansion of renewable energy.
- PPA stands for the “Power Purchase Agreement” model and refers to an agreement between a business that sells electricity to users (PPA provider) and the users of electric power. At Kirin Brewery, MCKB Energy Service Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Corporation Energy Solutions Ltd., acts as a PPA provider, installing megawatt-class solar power generation facilities on the roofs of breweries, while Kirin Brewery purchases and uses the power generated.
Use of solar power in Australia
Lion installed photovoltaic system to Castlemaine Perkins Brewery in 2019 and to Little Creatures Brewery in 2020.
Tooheys Brewery, the largest brewery in New South Wales, collaborates with Australian Hotels Association (AHA), contracting PPA with a renewable energy distributor.
By leveraging a buying power of Tooheys, AHA was able to introduce renewable energy at a lower price, successfully reducing the electricity unit cost for hotels’ pubs from 11.5c/kWh to 6.9c/ kWh.
In 2020, Lion became Australia’s first large scale carbon neutral brewer, certified by Climate Active*1. Lion discloses carbon credits used to offset its emissions for a year in the annual report to comply certification requirement by Climate Active. The requirement is a new standard for carbon neutral certification in Australia.
In New Zealand, Lion has obtained Toitū*2 carbon zero certification since 2021.
- A third-party certification body established by the government of Australia
- A third-party certification body established by the government of New Zealand
Renewable energy certificates
Since 2021, Kyowa Hakko Bio has introduced “Renewable Energy Certificates (I-REC)” at Thai Kyowa Biotechnologies in Thailand. This is the first case of I-REC application in pharmaceutical and food industries in Thailand. The initiative has offset emissions from electricity and reduced annual GHG emissions by 20,249 tonnes.
We have also introduced renewable energy certificates to Kyowa Hakko Kirin China Pharmaceutical and BioKyowa (I-REC and REC, respectively).
Wind power generation
Mitsubishi Corporation Offshore Wind Ltd., Venti Japan Inc., C-Tech Corporation, and Mitsubishi Corporation have been selected as power generation business operators for projects off the coast of Noshiro City, Mitane Town, and Oga City in Akita Prefecture, off the coast of Yurihonjo City in Akita Prefecture, and off the coast of Choshi City in Chiba Prefecture, through a consortium (the “Consortium”) represented by Mitsubishi Corporation Energy Solutions, Ltd.
Kirin Holdings is a partner in the Consortium. These projects are Japan's first fixed-bottom offshore wind power generation projects in general sea areas. Both projects will be the largest power sources in Japan and will make a significant contribution to the Japanese government's commitment to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. The maximum power output of the three projects will be approximately 1.69 million kW, which is sufficient to meet the electric power demand of approximately 1.21 million households.
Production
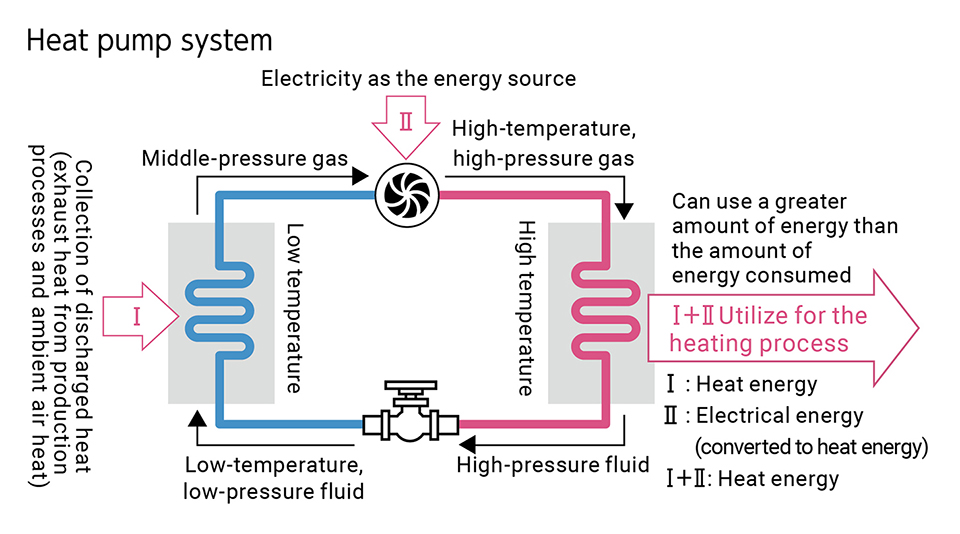
Use of heat pumps in production processes
The Kirin Group must improve energy efficiency and reduce the amount of energy consumption. At the same time, we believe that reducing dependency on fossil fuel combustion in production sites, and increase that on electricity, and, furthermore, using renewable electricity are the most effective ways of reducing GHG emissions.
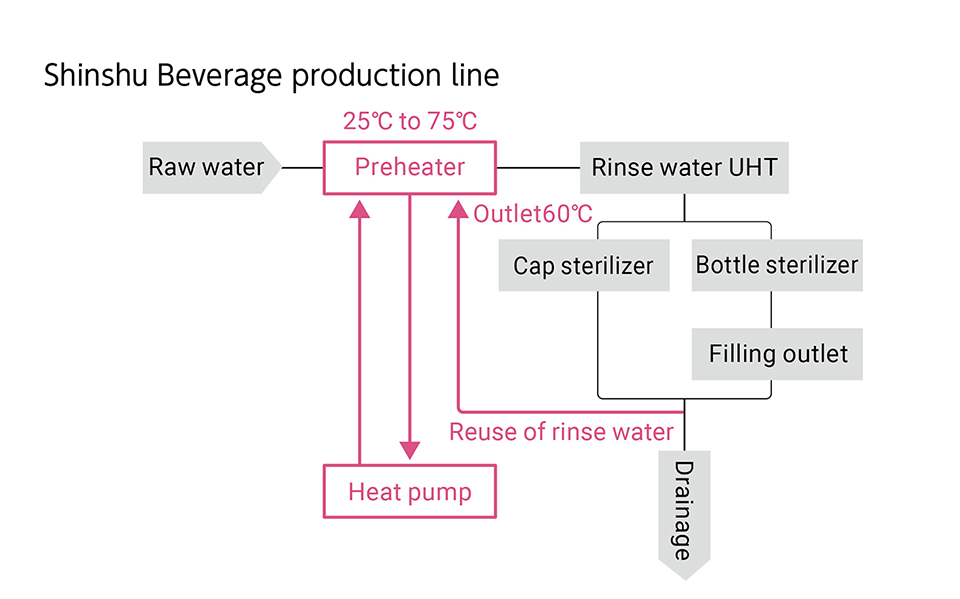
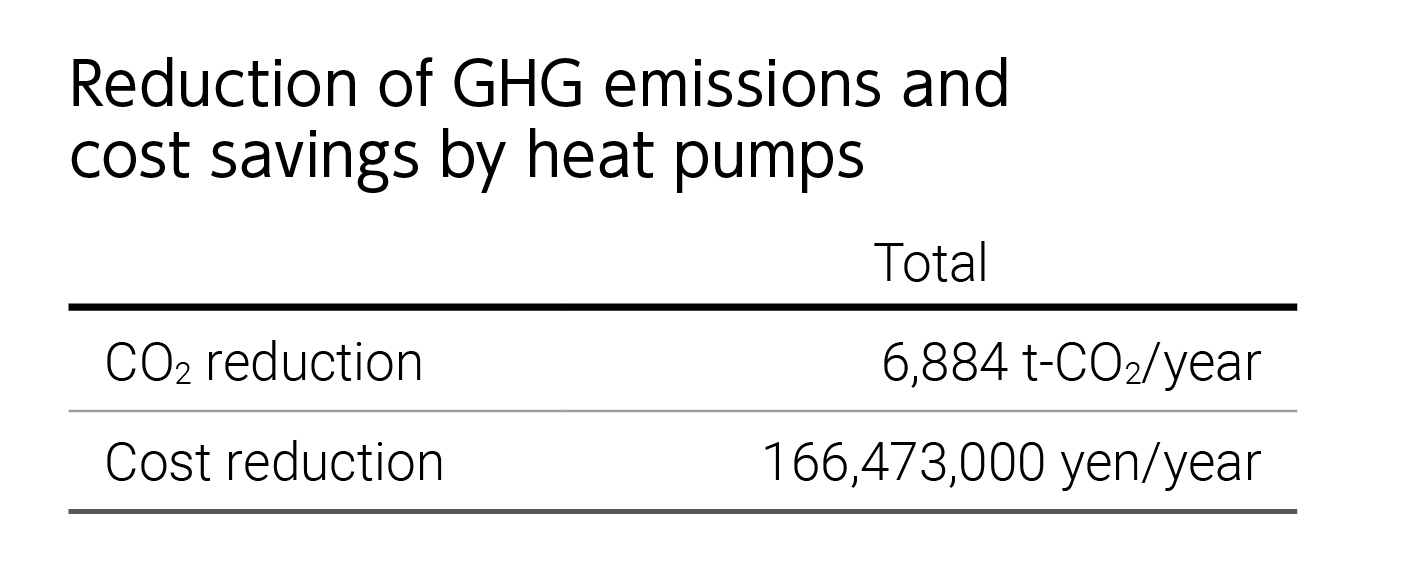
Kirin Brewery has successfully reduced its GHG emissions by approximately 70% over the 25 years from 1990 to 2015. In 2019, we introduced heat pump systems at the wastewater treatment facilities of six Kirin Brewery plants, thereby reducing GHG emissions by 3% (approximately 4,800 tonnes) from the previous year across Kirin Brewery as a whole (as of November 2023). At Shinshu Beverage, we reuse waste heat, which is difficult to use directly in rinsing processes for bottles and caps, through a heat pump unit, enabling us to reduce GHG emissions by approximately 970 tonnes per year. The Kirin Brewery Okayama Plant has reduced annual GHG emissions by approximately 180 tonnes by reusing waste heat and using thermal energy of atmosphere to a hot water sterilization process for cans.
Fuel conversion
The majority of the fuel we use at breweries are consumed in boilers that generate steam. At all plants of Kirin Brewery and Kirin Beverage, we completely converted the fuel to natural gas, which generates less GHG emissions than heavy oil. We have achieved more efficient boiler operations through installation of highly efficient gas boilers. To meet part of the plant's heat and electricity needs, cogeneration systems have been installed to provide both heat and electricity.
Lion is planning to install an electric boiler at a brewery in New Zealand, which will begin operation in late 2025. It will save approximately 700 t-CO2-e per year (6% of Lion Scope 1 and 2 emissions in New Zealand) by replacing the current LPG fuel.
-

Cogeneration
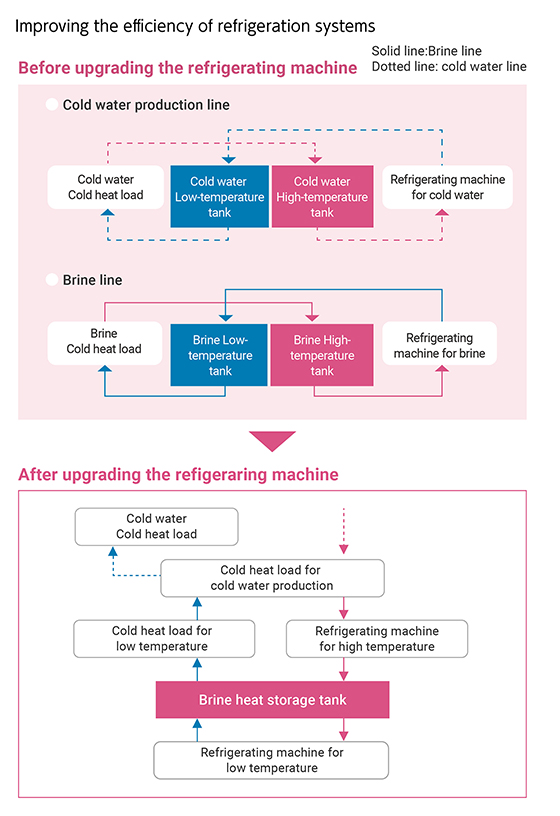
Improving the efficiency of refrigeration systems
At Kirin Brewery, we reduce energy consumption through improving the efficiency of refrigerating systems. We are introducing a cascade refrigeration system, which cools cooling media in multisteps, a methodology to maximize energy efficiency of refrigerators.
Containers and Packaging
Reduction of GHG emissions during transportation by reducing containers and packaging weight
Making containers and packaging lighter leads to reducing GHG emissions from production and transportation of the containers and packaging. Kirin Brewery and Kirin Beverage reduced GHG emissions from containers and packaging by a total of 5.3 million tonnes* by reducing the weight of containers and packaging between 1990 and 2021.
- Calculated based on the Carbon Footprint Product Category Rule (Certified CFP-PCR Number: PA-BV-02) applied to the actual containers and packaging usage of Kirin Brewery and Kirin Beverage from 1990 to 2021.
Logistics
We are promoting joint deliveries and modal shifts
The Kirin Group regards logistics as a noncompetitive sector and is actively engaging in initiatives together with other companies in the same industry.
In 2017, Kirin Brewery and Asahi Breweries opened a joint delivery center in Kanazawa City, Ishikawa Prefecture, and launched joint train transportation from plants in western area of Japan. Neither of the companies has plants on the coastal side of Japan Sea, so products previously had to be transported by truck over long distances—of 200 km—from their plants on the Pacific Ocean side.
This logistic was inefficient and heavy burdens for truck drivers.
Joint transportation using train containers not only reduced significant GHG emissions but also shortened driving distances of trucks, significantly reducing burdens of drivers. Thus, the joint delivery contributes to solve capacity shortages of logistic industry, one of the biggest issues in Japanese society. Through these efforts, we have successfully completed modal shifts from long distance truck transportation, equivalent to 10,000 vehicles a year, to railway containers, and we estimate that we can thus annually reduce GHG emissions by approximately 2,700 tonnes.
In September 2017, we began joint delivery with Asahi Breweries, Suntory, and Sapporo Breweries in the eastern Hokkaido area. We estimate that the Hokkaido case results in a reduction in annual GHG emissions of approximately 330 tonnes. *
Kyowa Kirin also applies joint deliveries and its Ube Plant utilize railway container transportation for raw material logistics.
The Kirin Group is actively pursuing modal shifts of switching from truck transport to rail and ocean transport, which has lower GHG emissions, for long-distance shipments (400 to 500 km or more).
In April 2024, KIRIN GROUP LOGISTICS, Japan Freight Railway, and NIPPON EXPRESS implemented modal shifts for the Kirin Group's products equivalent to approximately 84,000 t-CO2 (7,000 10 ton trucks, equivalent to approximately 17,000 five-ton containers) per year. This initiative is expected to reduce annual emissions by approximately 3,130 t-CO2.
- Contribution to Avoided Emissions through the Global Value Chain, Fifth Edition, Keidanren (Japan Business Foundation)
Vendor-managed warehouse
The use of vendor-managed warehouse can reduce long-distance transportation. As a result, GHG emissions are reduced, contributing to more sustainable supply chain.
With the aim of mitigating the risk of not being able to transport due to an unavailability of trucks and optimizing transportation efficiency, we started a trial operation of raw materials procurement and distribution system using raw materials warehouses (vendor-managed warehouses) close to Kirin Beverage’s plants, Shonan Plant and Shiga Plant, in October 2019. By establishing vendor-managed warehouses, raw material and ingredient suppliers can transport desired amount of raw ingredients with their convenient schedules, thereby maximizing efficiency. This initiative has made it easier for plants to cope with sudden changes in production plans and contributed greatly to improving production flexibility.
Sale
Introducing “heat pump-type vending machines” as a pioneer of an industry and expanding the use of green power vending machines
Kirin Beverage is the first in the industry to introduce heat pump-type vending machines in 2006, and from 2012, almost all newly installed vending machines for cans and PET bottles are of this type. As of March 2024, we have switched more than 90% of installed vending machines to this type.
Heat pump-type vending machines pump up waste heat generated from cooling functions and use the heat to warm up the products.
This system reduces electricity consumption compared to conventional vending machines.
Some models offer higher energy-saving performance with heat source not only by recovering waste heat released by the cooling function but also by capturing heat from outside the machine and with improved insulation performance by effective use of vacuum insulation materials. These vending machines have evolved to the point where electricity consumption can be reduced by about 40% compared to 2013. Installation of the new models began in 2015, and we are aiming for approximately 90% of the new machines we install in 2024 to be new models.
Since January 2024, we have been expanding the use of green power vending machines to reduce Scope 3 emissions. This is an initiative to achieve net-zero GHG emissions by obtaining renewable energy certificates equivalent to the annual electricity consumption required for vending machine operation.
Carbon neutral beer
Steinlager, which Lion sells in New Zealand, has obtained certification as a carbon zero beer under the Toitu program by a body of the New Zealand government. In 2021, we featured the Toitu carbon zero mark in our marketing campaigns to highlight to consumers the commitment Lion has made to reducing GHG emissions through Steinlager and other products.
In May 2022, Lion began selling “XXXX Zero,” Australia’s first carbon neutral and alcohol-free beer. XXXX Zero has obtained carbon neutral certification in the form of Climate Active certification.
In Australia, Lion is preparing to acquire carbon neutral certification through Climate Active for many key products. In order to obtain certification, Lion is working to comply with the requirement that it must offset all GHG emissions from the complete life cycle of the product, including emissions from raw materials and packaging, distribution and product waste.
In 2020, New Belgium Brewing launched FAT TIRE ALE, the first carbon neutral beer in the United States. The carbon credits being purchased and amortized also contribute to economic support for converting farmers to regenerative agriculture.
New Belgium Brewery has created a beer called TORCHED EARTH ALE to show consumers what the future of beer might look like if climate change progresses. By showing consumers the taste of beer made from ingredients likely to be available in a future where climate change has progressed, the company is drawing attention to the importance of carbon-neutral products.
- Carbon neutral beer is referred to as "carbon zero beer" to match the name on the certification.
Supply chain
Cooperation with business partners
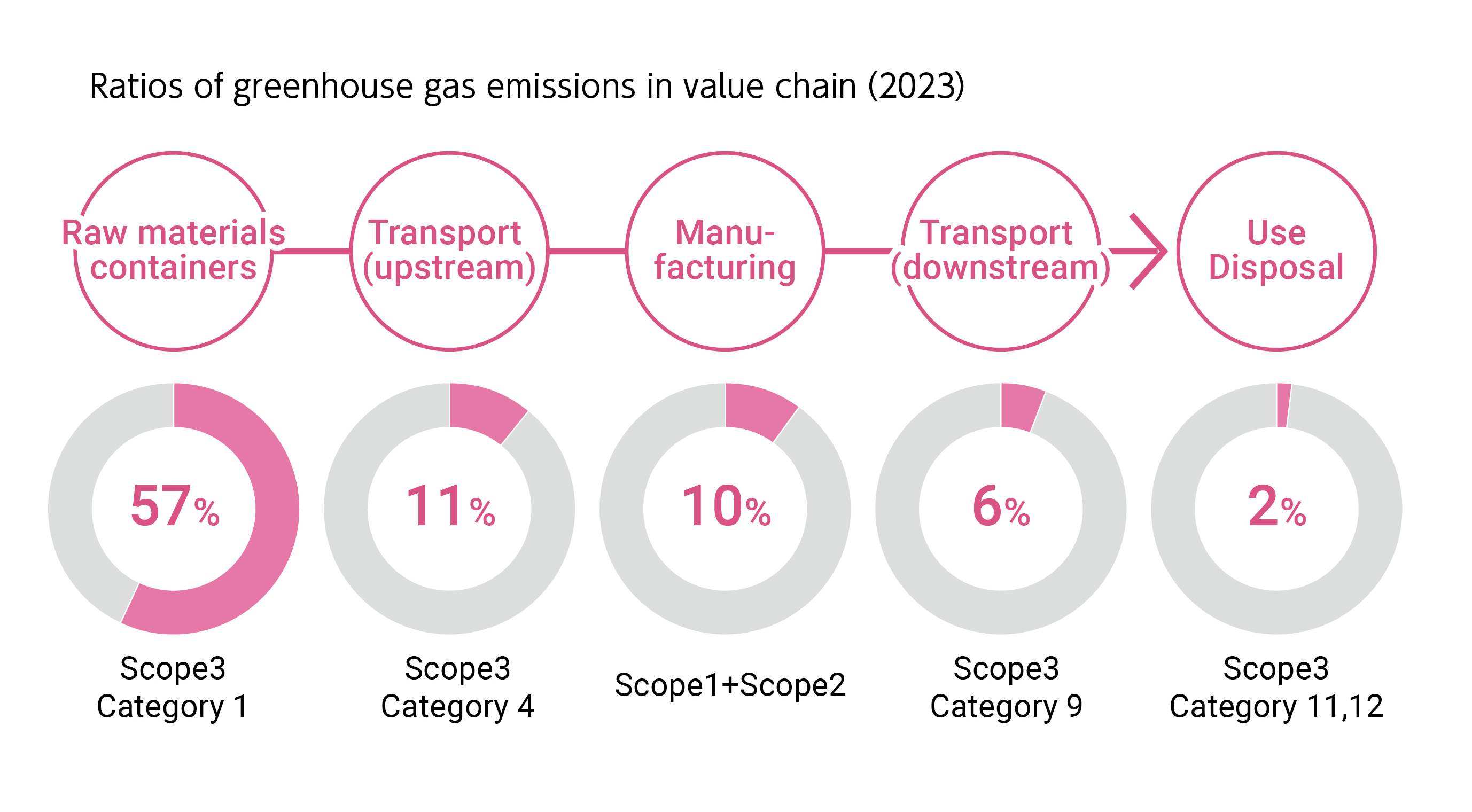
Of the categories in the “Scope 3 Standard” of the GHG Protocol, we will focus our efforts on Category 1 (purchased goods and services), which accounts for about 60% of the Kirin Group's Scope 3 emissions, followed by Category 4 (upstream transportation and distribution) and Category 9 (downstream transportation and distribution), which account for the next largest shares of emissions. In this way, we work to reduce emissions across value chain while prioritizing engagement and collaboration, through the “encouragement of reduction at business partners,” as well as the “reduction by our controllable measures.”
We have requested that all suppliers comply with the Kirin Group Sustainable Supplier Code, which includes measures to address climate change. Furthermore, in April 2024, we launched the Supply Chain Environmental Program. Through these efforts, we will strengthen cooperation with suppliers that have large GHG emissions, and promote activities in three main areas: mutual disclosure of actual GHG emissions data, target-setting requests and support for reducing GHG emissions in line with SBT levels, and cooperative efforts to reduce GHG emissions. We expect these efforts to contribute to a reduction of 10%, or one-third of our medium-term target to "reduce overall GHG Scope 3 emissions by 30% from 2019 levels by 2030."
Lion is a member of the Australian Climate Leaders Coalition, a group of CEOs of Australian companies.
For various reasons, it is difficult for suppliers, retailers, and other companies along their value chains to disclose actual data on their GHG emissions to each other. In response to this issue, the coalition adopted a system of pooling actual data to a thirdparty without mutual disclosure among the companies, and thus confirmed that the pooling system was able to identify Scope 3 emissions more accurately. These efforts started the conversation on how stakeholders in the value chains could work together to reduce emissions, which will result in higher Scope 3 reduction targets and contribute to highly effective actions. In addition, we are calculating the CFP per product and utilizing it to visualize GHG reduction status and set targets throughout the supply chain. The Australian Climate Leaders Coalition has published these approaches as part of the “Scope 3 Roadmap.”