Environmental management system
Environmental management and CSV
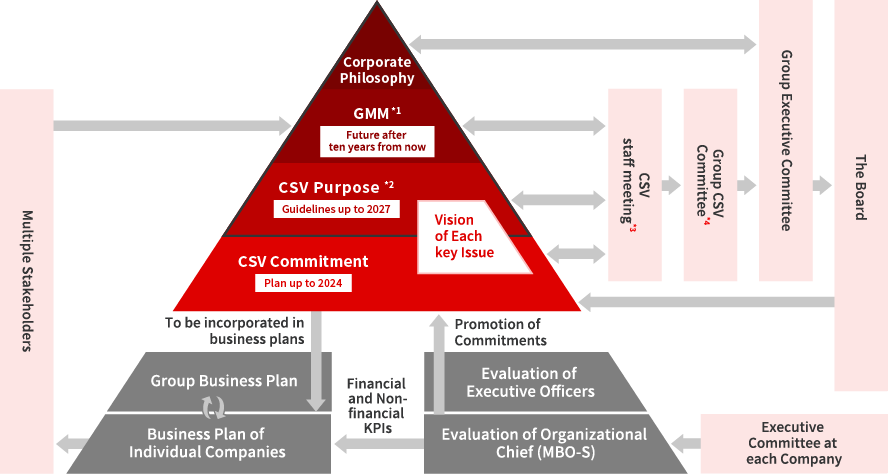
The Kirin Group engages in environmental management as part of its CSV management system. The Kirin Group has organized material issues, including the environment, as “Kirin Group’s management issues for sustainable growth (Group Materiality Matrix: GMM)”, as part of its commitment to sustainable development in partnership with society. We have set forth the following four issues as material issues related to the environment: “sustainable use of biological resources,” “sustainable use of water resources,” “sustainable recycling of containers and packaging,” and “overcoming climate change.” These issues are also consistent with the four priority themes of the Kirin Group’s Environmental Vision 2050. To create shared value with society and promote sustainable growth, in our CSV Purpose developed as the guideline for the Long-Term Management Vision, KV2027, we set our purpose for the environment in line with the Kirin Group’s Environmental Vision 2050: Enrich the sustainable Earth for future generations through positive impact. In response, Group companies have established CSV Commitments as mid-term targets to achieve our environmental vision and are using them as performance indicators. As we look to achieve our Environmental Vision, Purpose, and Commitment, the Kirin Group will gather the opinions of stakeholders in an appropriate manner, identify and assess the risks and opportunities related to the environmental activities of our businesses, and take necessary action from medium to long-term perspectives.
Disclosure based on TCFD recommendations
Governance Structure
- Group Materiality Matrix
- Translate management philosophy into social significance.
- Members: KH functional units Planning staffs, major operating companies’ Planning staffs
- Chair: The CEO and COO of Kirin Holdings (KH)
Members: KH functional units Director, The CEO of major operating companies
Environmental management systems
We believe that the establishment and proper operation of environmental management systems will enable us to prevent pollution to the natural environment.
In order to manage of legal requirements, we strictly manage records of revisions and abolishments at each business site, and we set voluntary management standards that are stricter than those set by laws and regulations, thereby thoroughly working to prevent environmental pollution. In addition to general pollution and health and safety issues, legal requirements include responses to waste and the Cartagena Protocol.
We operate environmental management systems to maintain compliance with these laws and regulations, and we have provided for these environmental management systems in the Principle for Kirin Group’s Global Environmental Management (KGEMP).
Under the KGEMP, a Group general environmental manager has been appointed as the chief executive officer for all Group environmental matters. As of April 2023, this role is held by the Senior Executive Officer of Kirin Holdings Company, Limited with responsibility for CSV strategy. The KGEMP requires the appointment of a general environmental manager, who has responsibility and authority for environmental matters in each operating company. In addition to monitoring to ensure that the company and its constituent companies are conducting their environmental activities appropriately, the general environmental manager conducts management reviews, identifies issues for improvement, and gives necessary directions to the relevant departments. In the event of an environmental crisis, the general environmental manager of each company will have full authority to resolve the crisis. The KGEMP stipulates that all business sites comply with laws and regulations and other rules relevant to the business’s environmental activities, reduce environmental load, such as GHG emissions and water intake, and prevent pollution. All business sites must also conduct internal environmental audits to ascertain the appropriateness and legal compliance of their systems and confirm how well targets are being met. The results of these audits will then lead into management reviews. We integrate the management of environment-related processes with company management processes in a manner suited to the companies’ respective regions. We incorporate environmental targets into goal-setting for each organization and individual, as well as responsible managers, and assess the degree to which those goals are achieved in assessments of performance.
Environmental audits
Each of the operating companies in the Kirin Group complies with ISO 14001 and other environmental management system standards. Internal auditing is conducted in each business location and constituent company, and the environmental management divisions in the head offices of each Group company conduct auditing of business locations and constituent companies. These audits lead to improvements in the individual companies’ environmental management systems.
In Japan, to guarantee further transparency and independence, we have been contracting an outside consultant to perform a strict environmental legal audit since 2009.By 2014, all brewing and manufacturing sites in Japan had been audited in one round, and this has continued for all manufacturing sites since 2015.
Status of compliance with environmental laws and regulations
Each business location is thorough in its management of legal requirements through a ledger, and works exhaustively to prevent environmental pollution by establishing voluntary management targets that are more stringent than those required by the legislation. When an incident that constitutes an environmental accident occurs, an "Environmental Accident Report" is prepared in accordance with standards stipulated by each operating company and reported to Kirin Holdings.
We have established a system for the reporting of environmental accidents within the Group, in which we share hiyari-hatto (near-miss) examples and accidents that occurred within the Group and extend countermeasures to other sites. We use internal environmental audits to check the status of initiatives taken toward achieving environmental targets, see how measures to prevent environmental accidents and hiyari-hatto (near-miss) cases are being shared with operating companies and business sites, and confirm the status of legal compliance. In 2023, the Kirin Group has no significant accidents and violations affecting environmental pollution.
Appropriate management of waste
The Kirin Group is working toward its declared goal of the implementation and firm establishment of thorough appropriate management of waste. To this end, we established the Kirin Holdings Waste Management Rules and are promoting the appropriate treatment of waste within the common Group systems. These rules standardize contract templates and the frequency and contents of contractor audit programs, and by keeping an updated list of staff in charge of waste management, we provide education to all staff who require it, based on standardized textbooks.
In Japan, Kirin Holdings collectively manages information on all waste disposal contractors for the Group, so in the unlikely event that a problem arises, we can immediately search for and confirm details about the contractor, its permits, the waste it is being contracted to handle, and other details. We have standardized operations in this way so that anyone who is newly assigned to waste-related work will be able to perform it with certainty.
Recycling of waste ingredients
The spent grain from beer production still contains nutrients and is effectively used for cattle feed and culture media of mushrooms. Lion continues to supply brewer’s yeast for use as an ingredient in the Australian fermented food, Vegemite. Spent grapes from wine production are “turned over” for a period of one year in a compost heap on the company vineyard and reused as compost (organic fertilizer). Since livestock feed alone is not enough to process the shochu spnet grain generated daily, we try to avoid the grain to be waste as much as possible by using the grain as a raw material for compost or as a microbial nutrient source for activated sludge in paper mills.
Preventing air pollution
The Kirin Group strives to comply with all laws and regulations relating to air pollution in the various countries in which we operate. We have established voluntary standards that exceed those required by environmental legislation and are working to reduce our emission of atmospheric pollutants.
In Japan, in addition to complying with the Automobile NOx and PM Law, we are also working to improve transportation efficiency and loading efficiency, and to utilize modal shifts.
Preventing water pollution
The Kirin Group thoroughly complies with laws and regulations for preventing water pollution in each of the countries where we operate and minimizes wastewater loads by setting our own strict control values, which go beyond those required by environmental laws.
Preventing soil contamination
When selling assets, the Kirin Group conducts thorough investigations of soil contamination, responding as necessary.
Managing chemical substances
The Kirin Group manages its chemical substances appropriately based on the Act on Confirmation, etc. of Amounts of Release of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof (PRTR Act) and other relevant legislation. Due to the nature of its business, the Kyowa Hakko Bio Group is committed to reducing volatile organic compounds (VOC), which account for the majority of chemical substance emissions.
Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB):Managing appropriately and disposing progressively according to the law.
Asbestos:Managing and isolating appropriately and treating progressively according to the law.
Environmental Education
Environmental Training
To mitigate environmental risk, the Kirin Group conducts an ongoing program for environmental training for its employees.
This systematized training consists of training for environmental staff and training by job grade, including new employees. The training conducted at the Technical Talent Development Center has been opened to Kirin Group companies in Japan.
As part of new employee training, basic training sessions on wastewater treatment, waste management, etc. are provided. Training for those in charge of industrial waste is systematized and implemented by the Kirin Holdings CSV Strategy Department.
Raising environmental awareness within the Company
The Kirin Group uses in-house communications to expand the depth and breadth of interest in and understanding of the environment among employees. We utilize employee newsletters and the intranet, and at Group headquarters, use screen videos presenting Kirin’s environmental initiatives on digital signage, in order to deepen understanding among employees.
On June 1, 2021, we launched the “KIRIN Now” website for Group employees. As more employees work from home owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, we are using this website to provide up-to-date information from the Kirin Group in a format accessible to all Group employees, in accordance with changes in work styles. As part of this initiative, we are communicating with employees about the Kirin Group’s CSV activities, centered on the areas set forth in our CSV Purpose, i.e., “Health and well-being,” “Community,” “Environment,” and “Responsible alcohol producer,” in an easy-to-understand manner, and strengthening two-way communication through the use of comments and users’ ability to indicate that they are “excited” about posts.