Core technology that creates accurate value: A competitive strategy combining R&D expertise and IP strategies
May 31, 2024
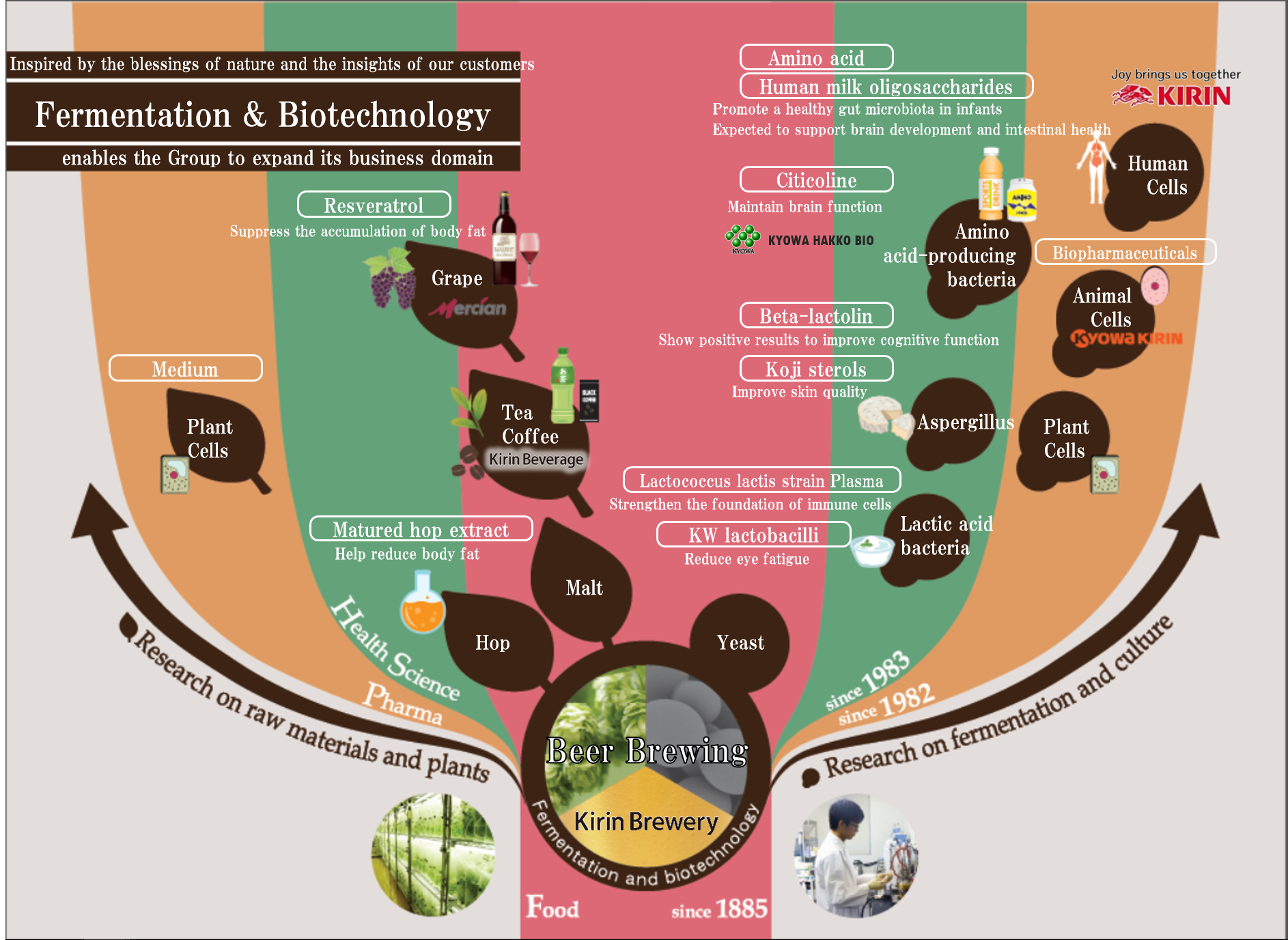
Core competencies of fermentation and biotechnology
We at the Kirin Group expanded our businesses, ranging from the Food & Beverages domain to the Pharmaceuticals domain. This expansion was based on our knowledge of raw material selection and processing and the fermentation and biotechnology that we developed through beer production. In the Food & Beverages domain, we conducted R&D aimed at creating new value in the beer category in Japan, where sales volume is expected to grow over the medium- to long-term. We did this in preparation for the integration of alcohol tax on beer. For example, we developed the “new carb-reduction production,” which achieved zero sugar through a review that began with the selection of malt and the advancement of mashing and fermentation technology. Using this production method, we launched KIRIN ICHIBAN Zero Sugar, Japan’s first*1 sugar-free beer. In the Health Science domain, we discovered Lactoccocus lactis Plasma (LC-Plasma) as a unique strain that supports the maintenance of immunity in healthy people, and then developed the iMUSE brand (soft drinks, supplements, and more), Japan’s first*2 functional food with immune function.
- First canned beer product in Japan that realized zero sugar (according to our research using Mintel GNPD)
- The first-ever Japanese brand to be publicly announced as foods with functional claims for immune function support.
An R&D system that supports technological capabilities
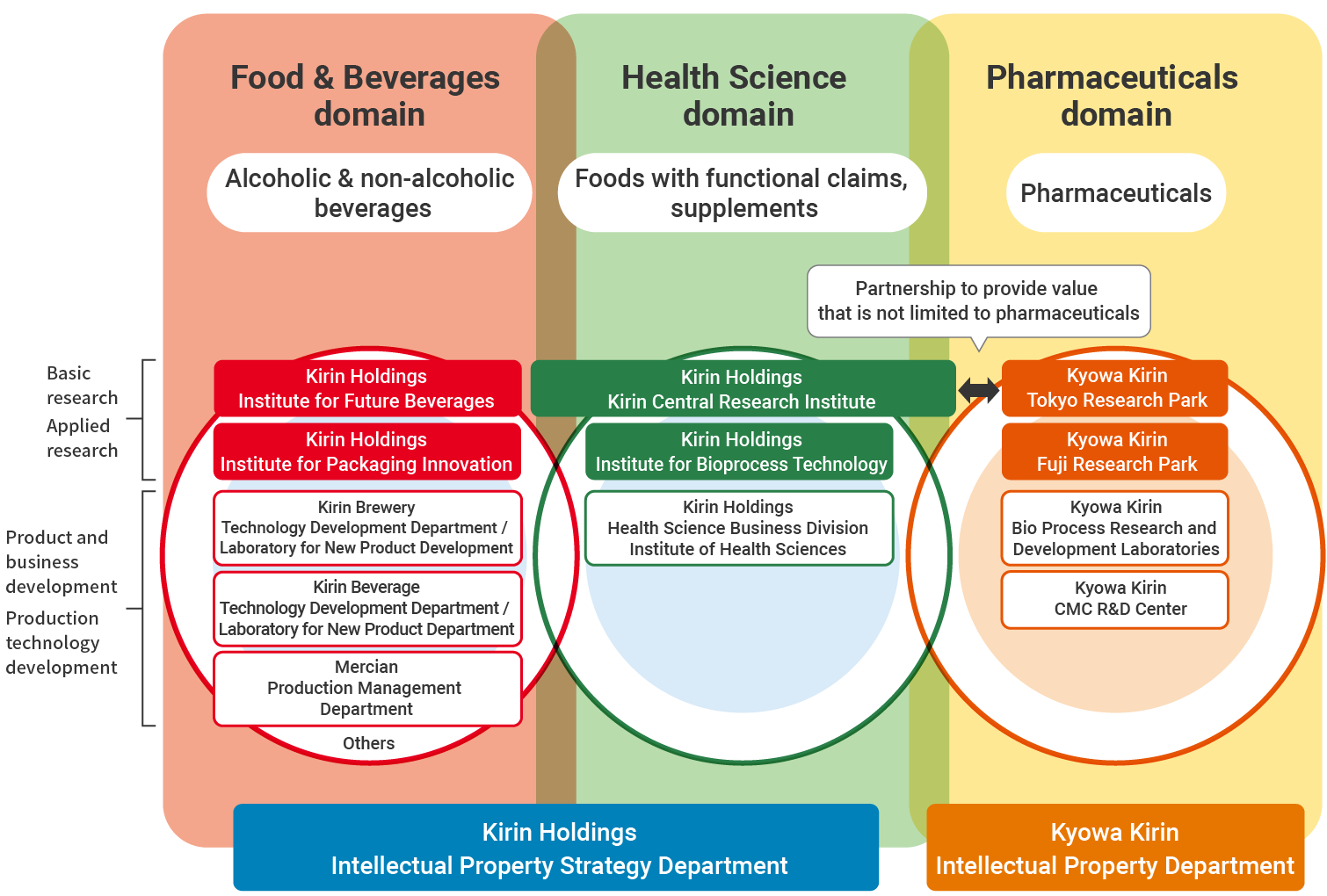
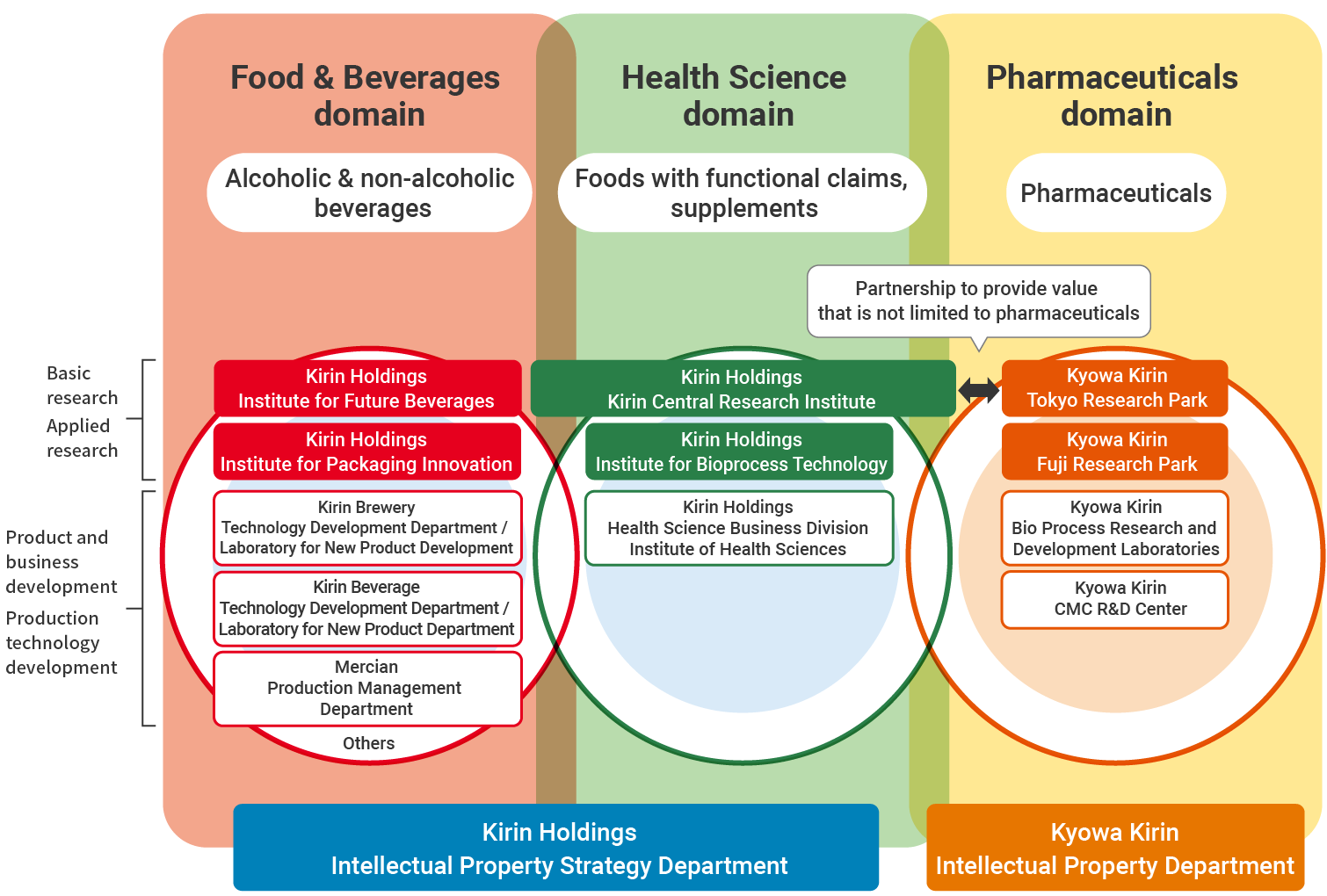
In the Food & Beverages and Health Science domains, Kirin Holdings’ research institutes are responsible for basic and applied research through the combination of human assets and technology. The R&D organizations for our businesses are responsible for the practical application of products and services based on the results generated by the research. In the Pharmaceuticals domain, Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., is at the center of R&D. The Technical Research Laboratory, the R&D organization of Kyowa Hakko Bio Co., Ltd., had a new start as Kirin Holdings’ Institute for Bioprocess Technology in 2024. Leveraging our production and engineering technologies for the mass production of functional materials through microbial fermentation, which we have developed so far, we will contribute to the expansion of the Health Science business.
Issues and progress since last year
Until now, the results generated at Kirin Holdings’ research institutes have been passed on to our businesses, and various products and services have been put to practical use at our operating companies. From 2023, we have been more conscious of creating innovation by solving social issues in the medium- to long-term. Furthermore, with the collaboration of business, R&D, and intellectual property, we are working to create R&D themes by increasing the level of collaboration between the three sections and through numerous discussions.
Pillars of strategy and initiatives
Advancing our initiatives with the collaboration of business, R&D, and intellectual property, we will simultaneously achieve R&D results and establish a competitively superior intellectual property portfolio. In particular, we will balance business and R&D strategies through collaboration and strategy formulation by operating companies and Kirin Holdings’ research institutes to create innovation in the medium- to long-term. Next, we will prepare a foundation for activities to create intellectual property and work to increase the volume and quality of patent applications. Kirin Holdings and Kyowa Kirin will continue to create collaborative themes to generate new value not limited to pharmaceuticals that can be carried out because of the fact that they are working together.
Example
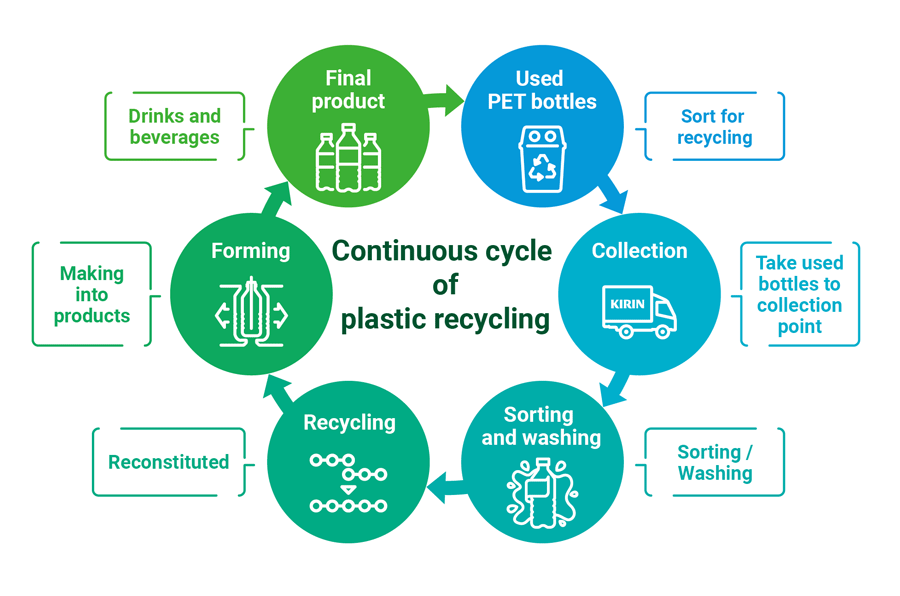
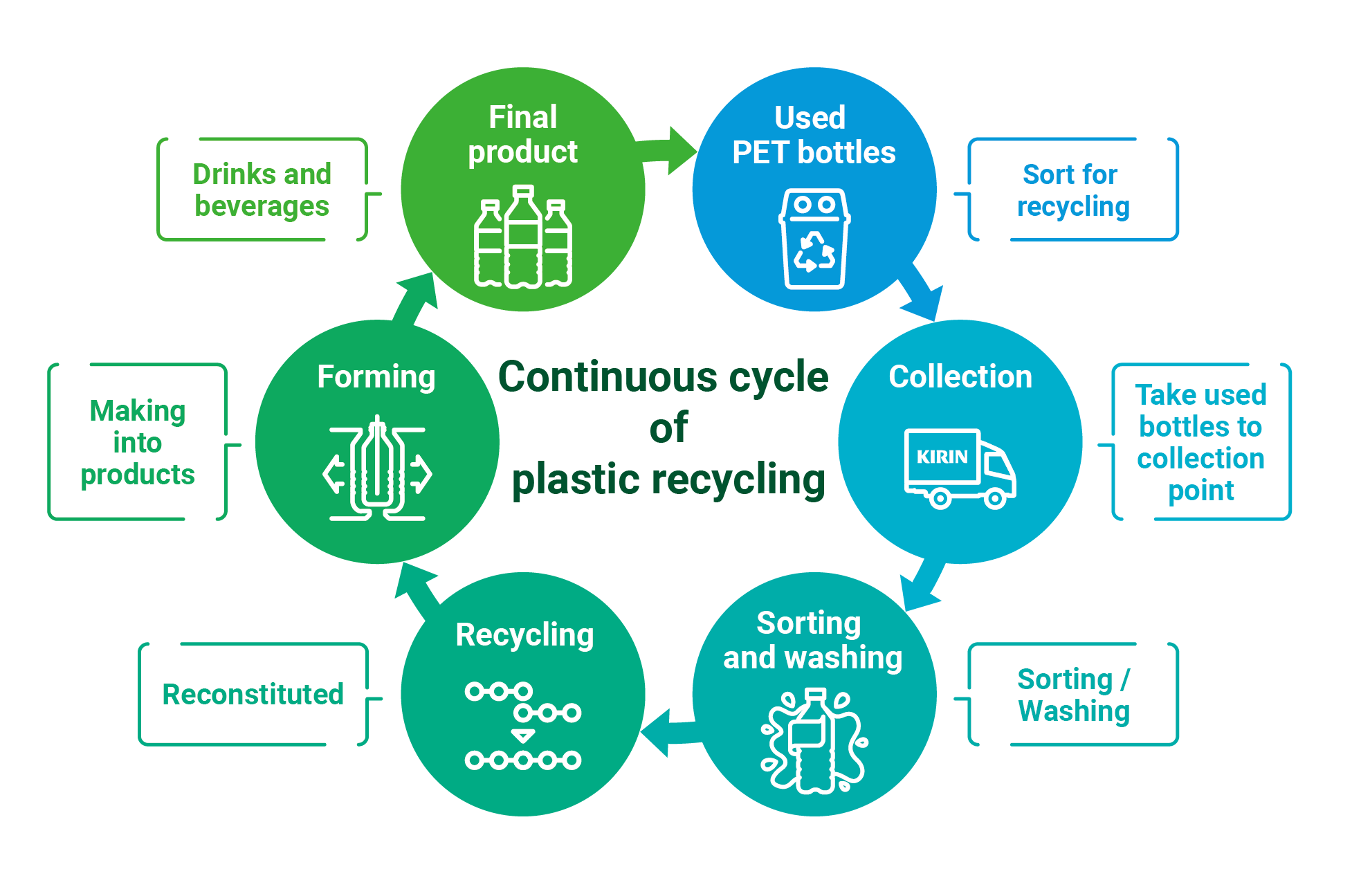
Establishing a cycle for plastics using PET chemical recycling system
As a solution for social issues that we will tackle in the medium- to long-term, we are working toward the commercialization of a PET*3 chemical recycling system to realize a society in which plastics can continue to be recycled. Concurrently with the R&D Department, we are working for technologies that will further enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. In 2023, we developed alkaline depolymerization, which achieves a faster, more energy-efficient PET decomposition process than conventional methods.
Furthermore, through joint research with Waseda University, we developed a refinement method through electrolysis that achieves both reduced environmental impact and reduced costs for the process to refine single molecules after PET decomposition. Leveraging the Kirin Group’s core technologies of fermentation and biotechnology, we are also working on the joint development of a PET decomposition technology using enzymes with Shizuoka University.
- Polyethylene terephthalate
Example
Contributing to the expansion of value of the LC-Plasma business with the coordination of business, R&D, and intellectual property
The Kirin Group aims to make intellectual property the driving force for the achievement of sustainable growth. From 2023, the IP department and top management, including domestic subordinates, periodically hold discussions for this achievement. The top management learns about the current status and results of intellectual property activities and discusses how to address issues identified through the review of previous activities. The decisions of the discussions will be reflected in the next plan of intellectual property activities as resources for the plan will be allocated appropriately. These continuous discussions will accelerate our collaboration among business, R&D and intellectual property.
To properly implement the intellectual property activities that have been decided, it is important to develop the human assets who create intellectual property and foster a culture that considers IP important. Based on each career stage and level of intellectual property literacy, the Kirin Group continuously reviews and implements training systems for intellectual property in each domain and department. For the human assets expected to create inventions in R&D departments, the motivations for creating intellectual property in each department are boosted by accompanying on-the-job training.
For a specific example of intellectual property activities for the LC-Plasma business, we are pursuing basic patents for the use of LC-Plasma in addition to establishing a patent wall with these basic patents as the core. Furthermore, recent applications such as a patent application (international patent application), including the results of clinical research related to COVID-19 announced in April 2023, have contributed to the growth of value possessed by LC-Plasma. According to analysis of the patents related to immune-related lactic acid bacteria technology filed by other Japanese food and beverage companies (provided by PatentSight®), these results show that the technology relevance of our basic patents remains at a high level and these patents serve as the foundation of our business for the expansion of the LC-Plasma.